Two-Stage Exams: Mixing Independent and Collaborative Assessments
Courtesy of Joss Ives
Goals:
To describe the benefits of the two-stage exam
To discuss different ways that instructors can implement the process
Background:
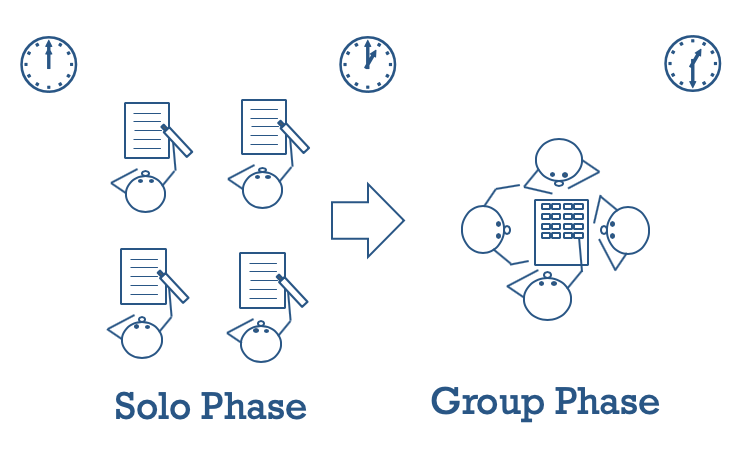
The two-stage exam is a process where students take an assessment independently and then take the same assessment or similar assessment collaboratively. It allows for both a way of assessing students’ individual learning as well as a way for them to enhance their learning with others through collaboration. Two-stage exams also incorporate all the benefits of collaboration like fostering an environment where students are actively constructing knowledge along with their peers, engaging with each other in worthwhile discussions and working as a group to justify their answers. Two-stage exams have been well-researched and provide the benefits of reducing student anxiety around testing, providing time for immediate feedback after exams, increasing retention rates of course content and enhancing higher order thinking for all levels of learners (Lusk & Conklin, 2003; Gilley & Clarkston, 2014; Mahoney & Harris-Reeves, 2019).
Recommendations:
Two-stage exams can take on a variety of formats. Here is a link to a quick video that shows instructors how to implement the process. Key takeaways are as follows:
- Students should take around 60% of the allotted time to do the work independently and then 40% of the time to work collaboratively. In a 50 minute class this means 30 minutes of independent time and 20 minutes of collaborative group work.
- Instructors can choose how to weigh exams but typically 85% of the grade comes from the independent exam and 15% from the collaborative portion.
- Groups can be formed ad hoc where students turn and work with the people next to them. Groups can also be designated by the instructor using sorting software like CATME or students can pick a partner they feel comfortable working with and then find another pair to form a group of four.
- To accommodate students that need extra time, instructors can work with the accessibility services to see if they can assist with the independent portion of the test.
- Instructors can make the collaborative part of the exam open book/open note to encourage accuracy.
- A few weeks after the exam, instructors can do a quick low-stakes or no-stakes assessment that measures whether or not students retained the information from the exam.
References:
Gilley, B. H., & Clarkston, B. (2014). Collaborative testing: Evidence of learning in a controlled in-class study of undergraduate students. Journal of College Science Teaching, 43(3), 83-91.
Mahoney, J. W., & Harris-Reeves, B. (2019). The effects of collaborative testing on higher order thinking: Do the bright get brighter?. Active Learning in Higher Education, 20(1), 25-37.
Lusk, M., & Conklin, L. (2003). Collaborative testing to promote learning. Journal of Nursing Education, 42(3), 121-124.